Science Illustration Gallery
These images all illustrate some aspect of Swift science. All images are from NASA E/PO, Sonoma State University, Aurore Simonnet.
Each image can be clicked for a larger version. Please note NASA's Image Use Guidelines.
Learn more about gamma-ray bursts.
Gamma-ray Burst Illustrations
Supernova Illustrations

Artist's rendition of a collapse of the core of a massive star, which has very little visible effect at the surface.

Artist's rendition of the twin beams of matter and energy that have eaten their way out of a dying star that will be seen by Earth observers as a gamma-ray burst.
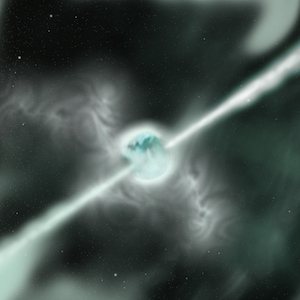
Artist's rendition of a dense magnetar, a neutron star possessing a magnetic field trillions or even quadrillions of times stronger that Earth's.

An instability develops in the outer layers of the blue supergiant, and it erupts violently, spewing out huge amounts of material at high speed. The star survives, but its time is nearing.

The star finally runs out of fuel, and the core collapses. The star explodes, ejecting material at speeds greater than 10 million miles per hour.

The wave of material from the supernova catches up with and slams into the slower, previously-ejected shell of gas. This creates a shock wave which, in turn, generates X-rays.
Neutron star Illustrations
Tidal Disruption Illustrations

An asteroid or comet too close to a neutron star being shredded. Gamma rays would be produced as the debris hit the star, as seen in this illustration.

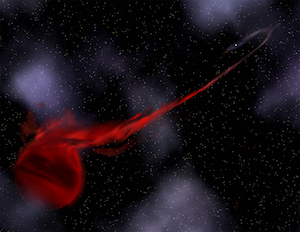
Artist's illustration of a star being torn apart due to tidal forces of a black hole resulting in a gamma-ray burst.
Black Hole Illustrations

An artist's conception of biggest stellar-mass black hole (upper left) pulling gas away from a companion Wolf-Rayet star.
Active Galactic Nuclei Illustrations
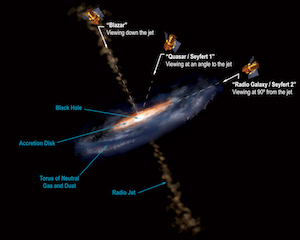
Illustration of the different features of an active galactic nucleus (AGN), and how our viewing angle determines what type of AGN we observe.
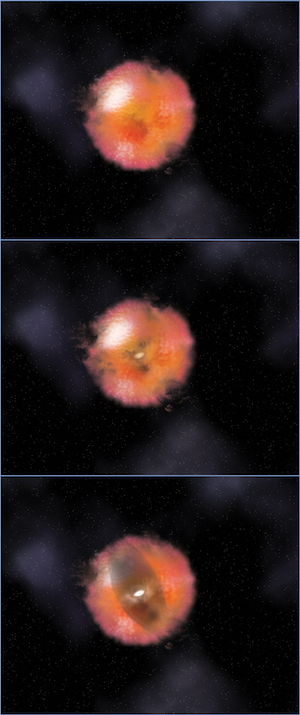
Artist's conception of a newly discovered type of AGN, one whose center is obscured by gas and dust. The two images below show cross-sections of what the inside of the AGN may look like.
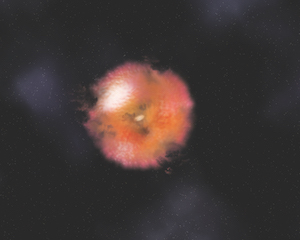
Artist's conception of a newly discovered type of AGN, one whose center is obscured by gas and dust.