Spacelab
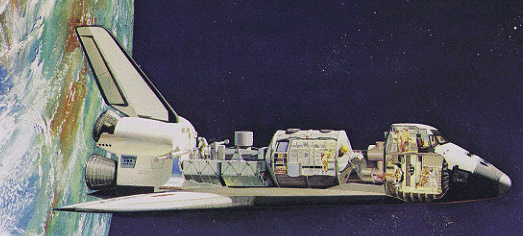
Cutaway illustration of the shuttle with a typical Space cargo. (Credit: NASA)
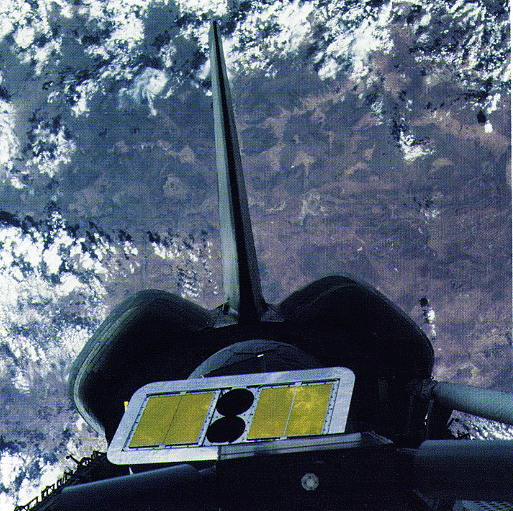
Photo of the X-ray Telescope on Spacelab 2 during the Space Shuttle flight (STS-51F). (Credit: NASA)
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory flown on the Space Shuttle to carry out scientific investigations. Spacelab flew on 22 Space Shuttle missions allowing scientists to conduct research in the microcragity of Earth's orbit.
Lifetime: November 1983 (first Spacelab mission flown on STS-9) - April 1998 (final Spacelab mission flown on STS-90)
Operators: NASA and the European Space Agency
Primary Science
The Spacelab missions were designed for a variety of scientific studies including atmospheric physics, solar observations, and deep space astronomy. In particular, Spacelab 1 and Spacelab 2 carried instruments that made observations of extra-solar high energy sources.
Spacelab 1
Lifetime: November 1983 - December 1983
Primary Science
Spacelab 1 was flown aboard Space Shuttle flight STS-9 and carried instruments to perform a multidisciplinary mission comprising five broad areas of investigation: atmosphereic physics and Earth observations, space plasma physics, astronomy and solar physics, material sciences and technology, and life sciences.
High Energy Science
Spacelab 1 carried an X-ray spectrometer to perform detailed spectral studies of cosmic sources and their changes over time.
Science Highlights
- Accumulated X-ray data for a dozen intended targest
Links to more information
Spacelab 2
Lifetime: July 1985 - August 1985
Primary Science
Spacelab 2 was carried aboard Space Shuttle flight STS-51F. It's primary objectives were to demonstrate Spacelab's capabilities through a multidisciplinary research program.
High Energy Science
One of the scientific experiments on Spacelab 2 was an X-ray telescope. Even though the shuttle failed to get to it's intended orbit, due to a premature main engine shutdown, the X-ray telescope performed as expected.
Science Highlights
- Seventy-five hours of observations including eight galactic clusters, the galactic center, and the Vela supernova remnant


