Sorting out Dark Stuff
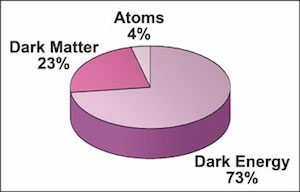
Image credit: NASA/ WMAP Science Teams
Astronomers have found that 4% of the universe is made of "typical" atoms, 23% of the universe is made of dark matter (which does not give off or absorb light), and 73% is made of dark energy (which is making the universe's expansion speed up).
There's good news and bad news about the universe. The bad news is that the matter which makes up everything that's visible – the Sun, the Earth, humans, everything we can directly detect – adds up to just 4 percent of the known universe. The good news is that we humans are beginning to get a handle on what makes up the rest of it.
The more abundant matter in the universe – dark matter – doesn't rule either. It makes up just 23 percent of the universe. This is dwarfed by the most abundant part of the universe – dark energy. Dark energy is 73 percent of the universe. While both are mysterious, and both have been dubbed "dark" because they can't be directly sensed, they are very different from each other.
Dark matter is the universe's "missing mass." It does not interact with normal matter, except to tug on it with gravity. Dark matter was first proposed in the 1930s by astronomers. They discovered that the amount of visible matter in galaxies wasn't enough to account for the measured gravitational effects of the galaxies on each other. Dark matter is currently thought to be a kind of cold particle that interacts extremely weakly with both atoms and light.
Dark energy, on the other hand, is a stranger idea. We can tell it exists, because it flings everything else apart. This odd energy is right now creating more space out of nothing and pushing everything further apart at a faster rate. And that's good news too, if you like privacy. •



