Media tagged with "image"
On most browsers, you can download the files by right-clicking on the download link and then chosing the "Save as..", or equivalent, option
Accretion Disk

Description: An artist's conception of the accretion disk in the binary star system WZ Sge. This system contains an accreting white dwarf star with a larger companion.
Credit: P. Marenfeld/NOAO/AURA/NSF
Type: Image
Keywords: accretion disk, white dwarf, type 1a supernova, image
Downloads
Accretion Disk 2

Description: An artist's conception of the accretion disk in the binary star system WZ Sge using data from Kitt Peak National Observatory and the Spitzer Space Telescope. This system contains an accreting white dwarf star with a larger companion.
Credit: P. Marenfeld/NOAO/AURA/NSF
Type: Image
Keywords: accretion disk, white dwarf, type 1a supernova, image
Downloads
The Big Bang
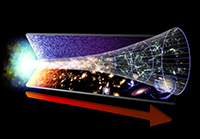
Description: A diagram representing the evolution of the Universe, starting with the Big Bang to present day. The red arrow marks the flow of time.
Credit: NASA/GSFC
Type: Image
Keywords: big bang, expanding universe, image
Downloads
Cosmic Microwave Background: 1965 view
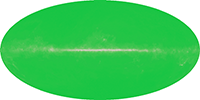
Description: An image showing the sky as would have been seen by the microwave receiver of Penzias and Wilson, if it could have surveyed the whole sky. This is a simulated image.
Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, image, holmdel horn
Downloads
Cosmic Microwave Background: COBE view
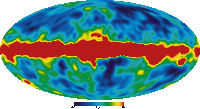
Description: Image showing the all-sky image produced by the 4 years of data from the COBE Satellite. The large red band is the microwave emissions from our own galaxy.
Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, image, cobe
Downloads
Cosmic Microwave Background: COBE Spectrum
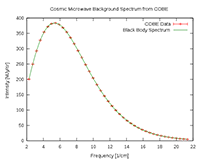
Description: A plot of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) spectrum in waves per centimeter vs. intensity. The solid curve shows the expected intensity from a single temperature blackbody spectrum, as predicted by the hot Big Bang theory. These precise CMB measurements show that 99.97% of the radiant energy of the Universe was released within the first year after the Big Bang itself.
Credit: Mather et al., 1994, Astrophysical Journal, 420, 439
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, image, cobe
Downloads
Cosmic Microwave Background: WMAP view
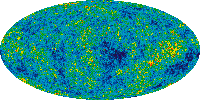
Description: An image showing the detailed, all-sky picture of the infant universe created from nine years of WMAP data. The signal from the our Galaxy was subtracted using the multi-frequency data.
Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, image, wmap
Downloads
Cosmic Microwave Background: History of Discovery
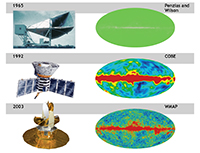
Description: Image showing the history of observations of the Cosmic Microwave Background. Top shows a simulated view that might have been seen by Penzias and Wilson in 1965, if they had been able to map the entire sky. The middle image shows the 4-year map from COBE data. The bottom image shows the 9-year map form WMAP. In each successive generation of observations, we see more detail in the background.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ESA
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, image, holmdel horn, cobe, wmap
Downloads
Cosmic Microwave Background: History of Discovery 2
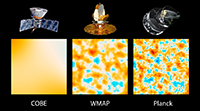
Description: Image showing the history of observations of the Cosmic Microwave Background from COBE to Planck. Each image shows a 10-degree square patch of the the all-sky maps made by each satellite. In each successive generation of observations, we see more detail in the Cosmic Microwave Background.
Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, image, cobe, wmap, planck
Downloads
Cosmic Microwave Background: Planck view
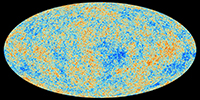
Description: An image showing the detailed, all-sky picture of the infant universe created from Planck data. Planck was launched by the European Space Agency in 2009, 8 years after WMAP was launched.
Credit: ESA and the Planck Collaboration
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, image, planck
Downloads
Energy Distribution of the Universe
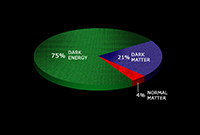
Description: Pie chart showing the distribution of energy in the universe by type: dark energy, dark matter, and normal matter. As shown in this illustration, dark energy is estimated to contribute about 75% of the energy in the Universe, dark matter about 21% and normal matter about 4%. Only the normal matter can be directly detected with telescopes.
Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss
Type: Image
Keywords: dark energy, image
Downloads
John Mather with Colleagues

Description: Image showing Dr. Mather (far left) and his colleagues at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center examining a map of the Universe. Dr. Mather won the 2006 Nobel Prize for Physics, awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Mather shares the prize with George F. Smoot of the University of California for their collaborative work on understanding the Big Bang.
Credit: NASA
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, john mather, image
Downloads
John Mather with COBE Results
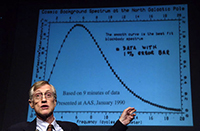
Description: Image showing Dr. Mather showing some fo the earliest data from the COBE satellite during a press conference. Dr. Mather won the 2006 Nobel Prize for Physics, awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Mather shares the prize with George F. Smoot of the University of California for their collaborative work on understanding the Big Bang.
Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, john mather, image
Downloads
John Mather at NASA

Description: Image showing Dr. Mather at NASA. Dr. Mather won the 2006 Nobel Prize for Physics, awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Mather shares the prize with George F. Smoot of the University of California for their collaborative work on understanding the Big Bang.
Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, john mather, image
Downloads
Spacecraft: COBE

Description: Image of NASA's Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) spacecraft. COBE was launched in 1989 to map the Cosmic Microwave Background for the first time.
Credit: NASA / WMAP Science Team
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, wmap, image
Downloads
Spacecraft: Planck

Description: Image of the European Space Agency's Planck spacecraft. Planck was launched in 2009 to map the Cosmic Microwave Background at a much higher sensitivity than WMAP.
Credit: ESA
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, planck, image
Downloads
Spacecraft: WMAP

Description: Image of NASA's Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) spacecraft. WMAP was launched in 2001 to map the Cosmic Microwave Background at a much higher sensitivity than COBE.
Credit: NASA / WMAP Science Team
Type: Image
Keywords: cosmic microwave background, wmap, image
Downloads
Timeline of the Universe
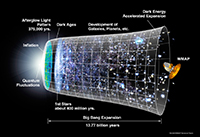
Description: Diagram showing a representation of the evolution of the universe over 13.7 billion years. The far left depicts the earliest moment we can now probe, when a period of "inflation" produced a burst of exponential growth in the universe. For the next several billion years, the expansion of the universe gradually slowed down as the matter in the universe pulled on itself via gravity. More recently, the expansion has begun to speed up again as the repulsive effects of dark energy have come to dominate the expansion of the universe.
Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team
Type: Image
Keywords: big bang, wmap, expanding universe, image
Downloads



